Gray Hydrogen Future in the Energy Transition
Gray hydrogen’s future in the energy transition is uncertain. As the world increasingly focuses on reducing carbon emissions, gray hydrogen is losing favor due to its high carbon footprint. Many countries have set ambitious targets to reach net-zero emissions by 2050, which requires a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
This has led to a growing interest in cleaner hydrogen production methods, such as green and blue hydrogen. As technology advances, the cost of green and blue hydrogen production is expected to decline, making it more competitive with gray hydrogen. In addition, many countries are offering incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of cleaner energy sources, which may further drive down the cost of green and blue hydrogen. The continued use of gray hydrogen in the energy sector will largely depend on the cost of producing and transporting it compared to cleaner alternatives.
Download – RequestForm (marketsandmarkets.com)
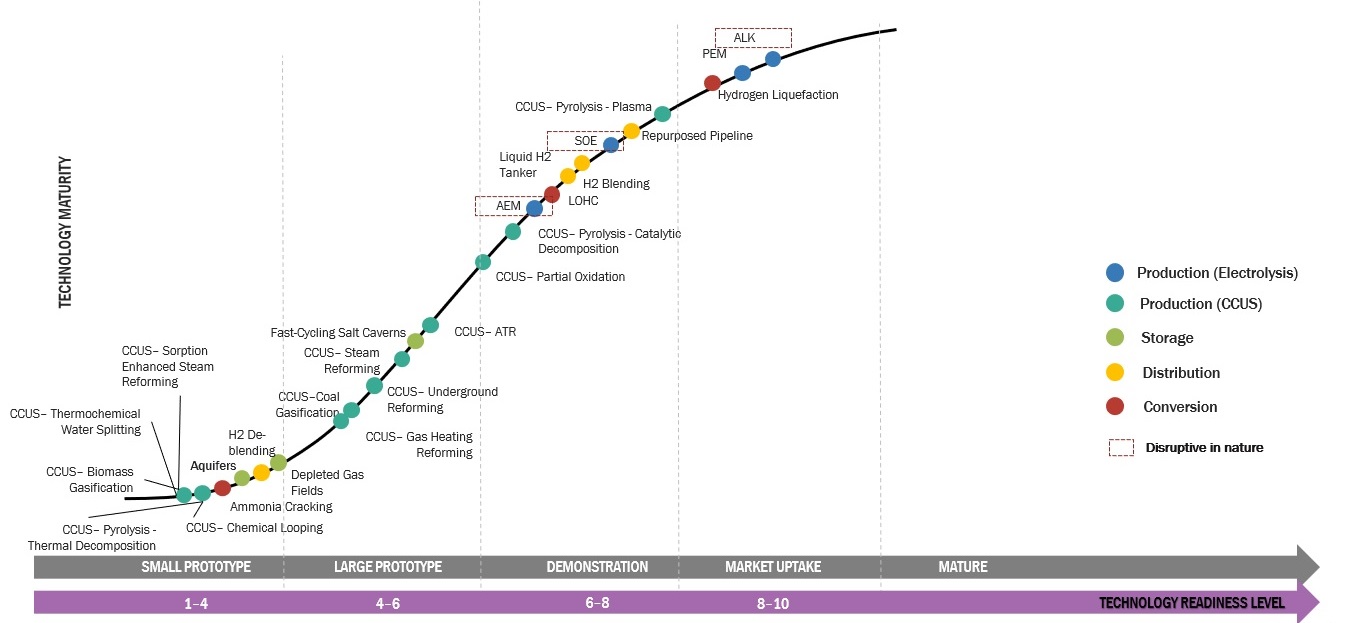
TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS IN GRAY HYDROGEN PRODUCTION
Gray hydrogen is the most commonly produced type of hydrogen worldwide. It is produced by steam methane reforming (SMR), a process that involves reacting natural gas with high-temperature steam to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide. However, the process also releases carbon dioxide (CO2), which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
In recent years, there has been increasing interest in developing new technologies to produce gray hydrogen in a more sustainable and environmentally friendly way.
Some of the notable technological developments in gray hydrogen future production include:
1. Carbon capture and storage (CCS): CCS is a technology that captures CO2 emissions from industrial processes and stores them underground or in other geological formations. By applying CCS to gray hydrogen production, it is possible to capture and store a significant portion of the CO2 emissions associated with the process, thereby reducing its environmental impact.
2. Blue hydrogen: Blue hydrogen is a type of hydrogen produced from natural gas using SMR, but with the addition of CCS technology. This process captures and stores the CO2 emissions associated with gray hydrogen production, resulting in a cleaner and more sustainable form of hydrogen.
3. Methane pyrolysis: Methane pyrolysis is a new process that involves heating natural gas at high temperatures to produce hydrogen and solid carbon. This process does not produce any CO2 emissions and solid carbon can be used as a valuable byproduct.
4. Electrolysis using renewable energy: Electrolysis is a process that uses electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. By using renewable energy sources such as wind or solar power, it is possible to produce gray hydrogen in a more sustainable and carbon-neutral way.
These technological developments have the potential to significantly reduce the environmental impact of gray hydrogen production and make it a more sustainable and viable option for the energy transition. However, it is important to note that these technologies are still in the early stages of development and will require further research and investment to become economically competitive with traditional gray hydrogen production methods.
Read more- Gray Hydrogen Future : High Growth Opportunities, Revenue Potential & Trends | MarketsandMarkets