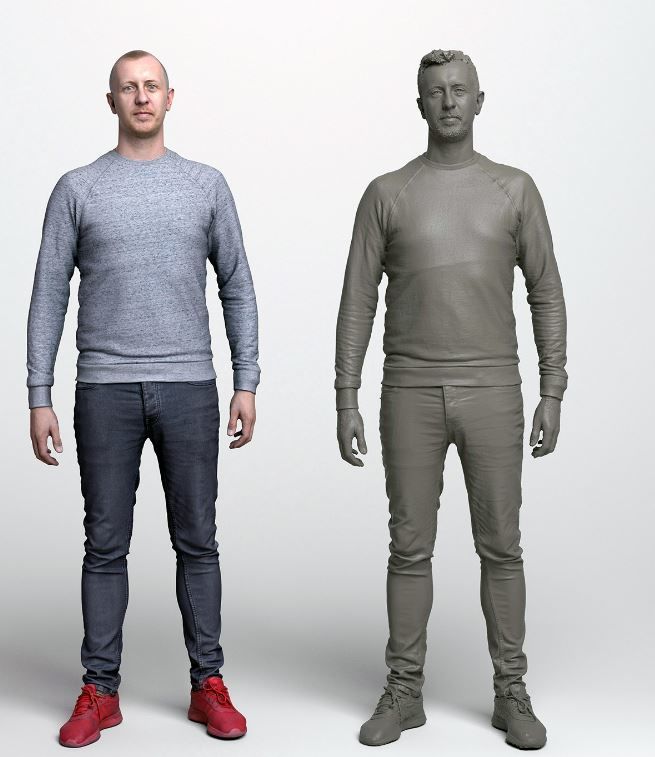
3D body scanners may sound like something from a science fiction movie, but they are increasingly popular in the healthcare industry. These machines provide a detailed and accurate look at a person’s body composition, which can be used to assess overall health and identify areas for improvement.
This article will explore how 3D body scanner is changing health assessments and their potential benefits and drawbacks.
What are 3D Body Scanners?
3D body scanners use specialised cameras to capture a three-dimensional image of a person’s body. These images can create a digital model of the person’s body, which can be analysed for various purposes. Several types of 3D body scanners are available, including handheld devices, full body scanner machine, and portable systems. They are used in multiple industries, from fashion and entertainment to healthcare.
How are 3D Body Scanners Used in Health Assessments?
In healthcare, 3D body scanner provide a detailed and accurate assessment of a person’s body composition. They can measure body fat percentage, muscle mass, posture, and more. These measurements can identify potential health issues and track progress over time. 3D body scanners are handy for athletes, as they can provide information about muscle imbalances and other issues that may affect performance.
One of the main benefits of using 3D body scanners for health assessments is their accuracy. Traditional assessment methods, such as callipers or body mass index (BMI) calculations, can be inaccurate and may not provide a complete picture of a person’s health. 3D body scanners, on the other hand, give a precise measurement of body composition and can identify areas for improvement.
Real-world Examples of 3D Body Scanner Use in Healthcare
Several healthcare facilities and organisations already use 3D body scanners for health assessments. For example, some hospitals use 3D body scanners to assess patients before and after surgery to track changes in body composition. Other organisations use 3D body scanners to determine the health of athletes and monitor their progress over time.
Case studies and patient testimonials demonstrate the effectiveness of 3D body scanners in healthcare. For example, one study found that 3D body scanners were more accurate than traditional assessment methods for measuring body composition in obese women. Patients also report feeling more confident and motivated to make lifestyle changes after seeing the results of their 3D body scan.
Future Implications and Advancements in 3D Body Scanner Technology
The future of 3D body scanner technology is bright, with many possibilities for improving medical diagnosis and treatment. For example, researchers are exploring using 3D body scanners to detect early signs of disease, such as cancer or osteoporosis. 3D body scanners may also be used to create personalised treatment plans based on a person’s unique body composition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D body scanner are changing how healthcare professionals assess and track a patient’s health. They offer many benefits, including increased accuracy and identifying potential health issues that traditional assessment methods may miss. However, there are also concerns related to their use, such as privacy and accuracy issues. As technology advances, we will likely see even more innovative uses for 3D body scanners in healthcare.


