Hydrogen technologies encompass a range of technologies and processes that involve the production, storage, distribution, and utilization of hydrogen as an energy carrier. Hydrogen, as the most abundant element in the universe, can be harnessed and utilized in various forms to meet energy needs while minimizing environmental impacts.
Download- RequestForm (marketsandmarkets.com)
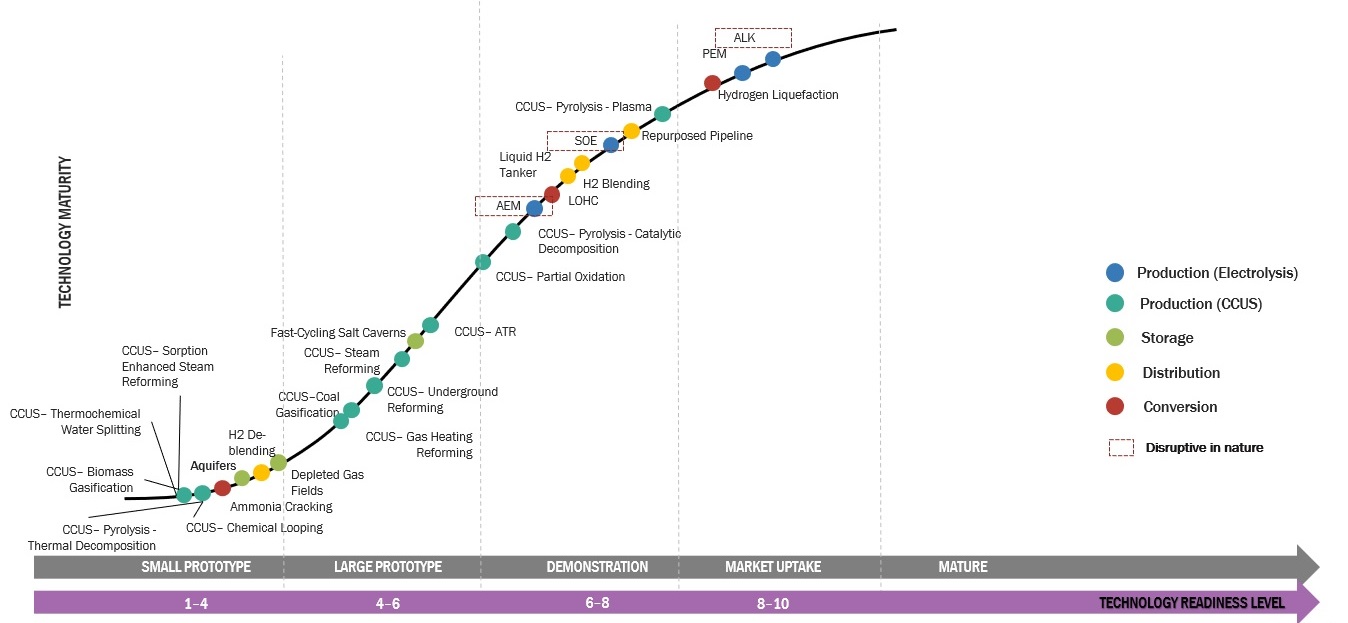
Hydrogen technology refers to the various uses and applications of hydrogen as an energy carrier and source. Hydrogen is a versatile element and clean energy carrier that can be used in a variety of ways to produce, store, and utilize energy. Here are some of the most used hydrogen technologies & comparisons of their advantages and disadvantages:
1. Steam Methane Reforming (SMR): SMR is the most common method of hydrogen production, accounting for approximately 95% of global production. It involves reacting methane with steam in the presence of a catalyst to produce hydrogen and carbon dioxide. SMR is a mature technology that is relatively inexpensive and efficient, but it produces carbon dioxide as a byproduct, which contributes to climate change.
2. Electrolysis: Electrolysis is a process that uses electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. If the electricity is generated from renewable sources, this can be a clean method of hydrogen production. There are two types of electrolysis: alkaline and proton exchange membrane (PEM). Alkaline electrolysis is a mature technology that is relatively inexpensive but less efficient than PEM electrolysis.
3. Biomass Gasification: Biomass gasification is a process that involves heating organic materials, such as wood or agricultural waste, in the absence of oxygen to produce a gas that can be purified into hydrogen. Biomass gasification is a renewable method of hydrogen production that can be carbon neutral, but it is relatively expensive and requires a significant amount of biomass feedstock.
4. Nuclear: Nuclear hydrogen production involves splitting water using high-temperature nuclear reactors. This method is a carbon-free way of producing hydrogen, but it is expensive, and there are concerns about the safety and security of nuclear reactors.
5. Photobiological: Photobiological hydrogen production involves using photosynthetic microorganisms, such as algae, to produce hydrogen. This method is a renewable and potentially carbon-neutral way of producing hydrogen, but it is still in the research and development phase.
6. Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells (SOEC): SOECs use a ceramic electrolyte to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. This technology is efficient, but it is still in the research and development phase.
7. Thermochemical: Thermochemical hydrogen production involves using heat and chemical reactions to produce hydrogen from fossil fuels or other sources. This method has the potential to be carbon neutral, but it is still in the research and development phase. Hydrogen can be produced through high-temperature processes, such as biomass gasification or high-temperature water splitting.