Green Hydrogen Economy
Growing at a 61.0% CAGR, the green hydrogen market is projected to reach $7,314 million by 2027.

Hydrogen, the universe’s most abundant element, has emerged as a pivotal player in the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions. Beyond serving as rocket fuel and a fundamental component of water, hydrogen has garnered considerable attention for its diverse end-use applications across various industries. This article delves into the manifold ways in which hydrogen end-use applications are reshaping the energy landscape, propelling us toward a more sustainable future.

Unit Economics Comparison of Hydrogen and Other Sources of Energy
Hydrogen’s unit economics, including cost, price, power output, and emission reduction, vary depending on factors such as the production method, hydrogen storage and transportation infrastructure, end-use application, and regional dynamics.
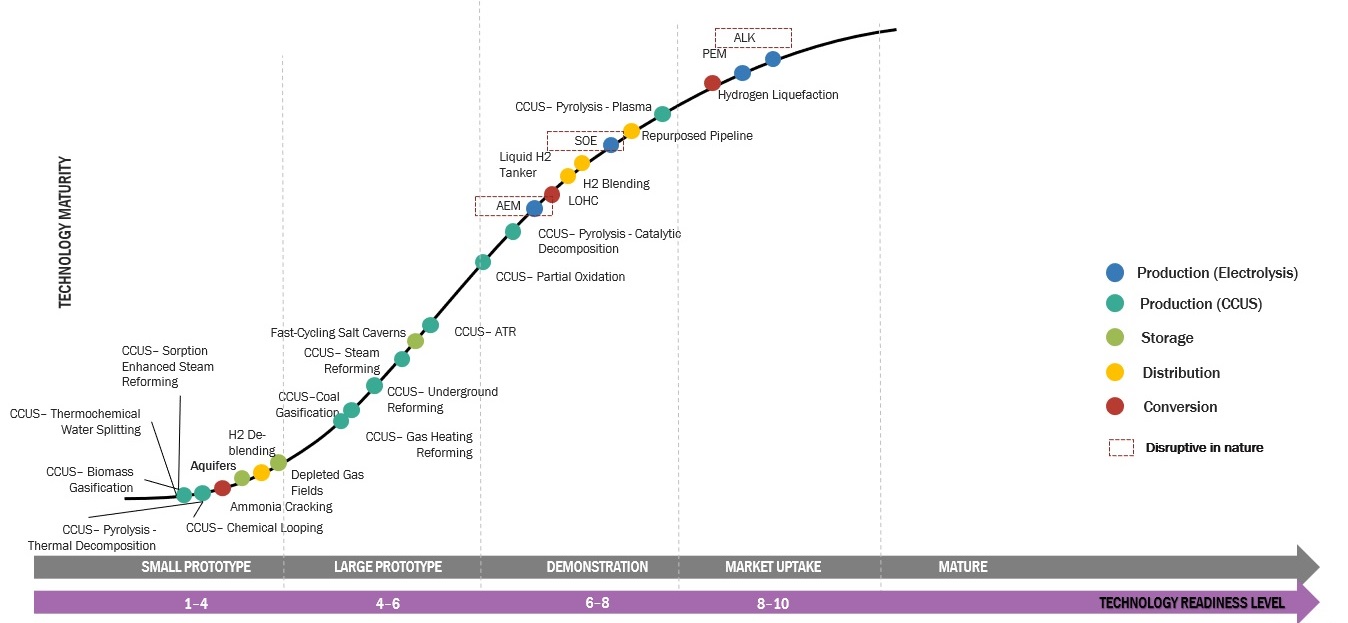
Green hydrogen is a type of hydrogen gas produced through electrolysis using hydropower, wind, or solar energy. This technique separates water (H2O) into its constituent parts, hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2), using electricity. Unlike gray or blue hydrogen, which is made from natural gas or fossil fuels, green hydrogen is produced without the release of carbon dioxide.

Green hydrogen is created through an electrolysis process utilizing sustainable energy sources, such solar or wind power. It has drawn a lot of interest as a clean, renewable energy source with lots of prospects in several industries.

The envisioned Hydrogen Future depends heavily on hydrogen as an energy carrier. Hydrogen presents various benefits that make it a valuable element of the energy landscape of the future. It is a clean, adaptable energy source.

The Hydrogen Paradigm is a forward-thinking energy plan that emphasizes using hydrogen as a clean, sustainable energy source. Recent years have seen a considerable increase in interest in hydrogen because of its potential to solve a number of environmental and energy-related issues.
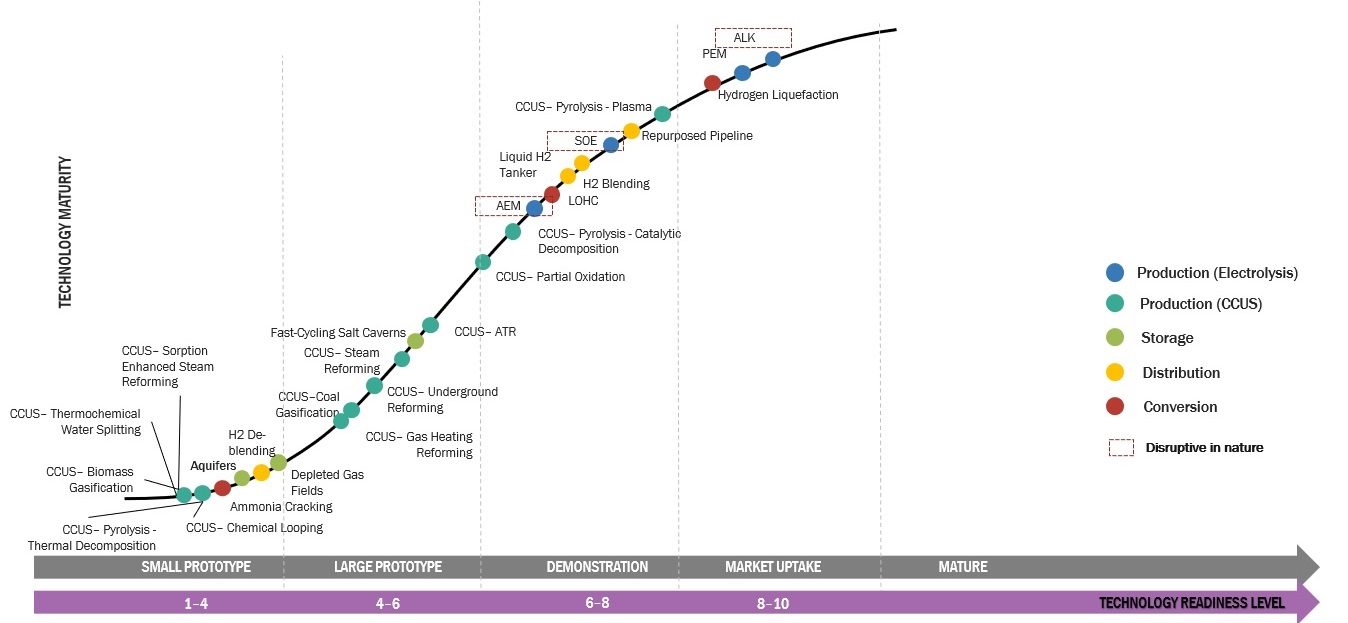
Green hydrogen is a form of hydrogen gas that is created by the electrolysis process utilizing renewable energy sources like sun, wind, or hydropower. Using electricity, this process divides water (H2O) into its component parts, hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2). Green hydrogen is created without emitting carbon dioxide, in contrast to gray or blue hydrogen, which is produced from fossil fuels or natural gas.

Green hydrogen is hydrogen produced using renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar power, through a process called electrolysis. It has gained significant attention as a clean and sustainable energy carrier with numerous opportunities across various sectors.

Both hydrogen and electricity have significant roles to play in the future of energy and transportation, depending on the particular application and context. However, this is a complicated and dynamic subject.