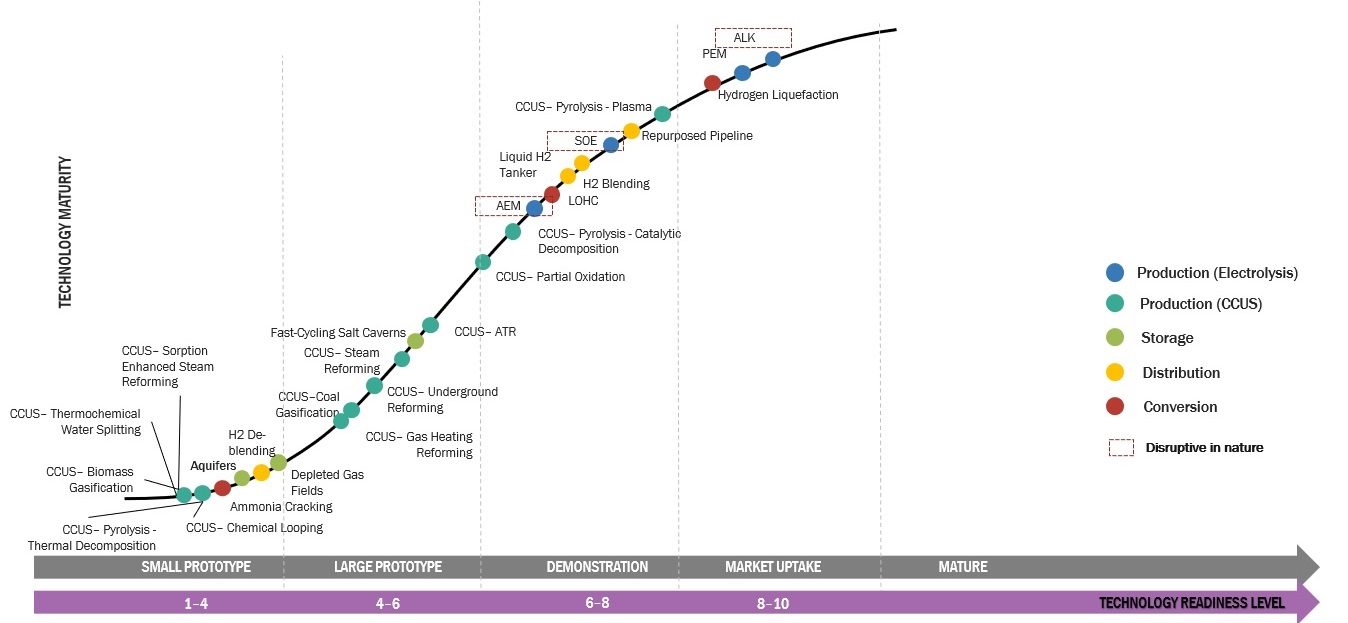
Green hydrogen is a form of hydrogen gas that is created by the electrolysis process utilizing renewable energy sources like sun, wind, or hydropower. Using electricity, this process divides water (H2O) into its component parts, hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2). Green hydrogen is created without emitting carbon dioxide, in contrast to gray or blue hydrogen, which is produced from fossil fuels or natural gas.
Download – https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/industry-practice/RequestForm.asp
Key characteristics and aspects of green hydrogen include:
1. Sustainability: Due to its reliance on renewable energy sources, which are carbon-free and have no effect on the environment, green hydrogen is seen as an environmentally benign and sustainable energy carrier.
2. Zero Emissions: It is crucial to the fight against climate change and the reduction of carbon footprints because its production method produces no greenhouse gases.
3. Clean Energy Storage: Green hydrogen has the potential to be a medium for energy storage. Hydrogen can be created from excess renewable energy and stored, transformed back into electricity, or used in a variety of ways as needed. This aids in addressing renewable energy sources’ sporadic nature.
4. Versatile Applications: Energy-intensive processes in industry can be made less carbon-intensive by using green hydrogen, and it can also be used for transportation (using hydrogen fuel cells) and heating (instead of natural gas).
5. Decentralized Production: Due to its local production, there is less demand for long-distance hydrogen transportation, enhancing energy security.
STRENGTHS AND LIMITATIONS OF GREEN HYDROGEN
Strengths of Green Hydrogen:
1. Renewable: Green hydrogen is a sustainable energy source that doesn’t add to greenhouse gas emissions because it is made using renewable energy sources like solar, wind, or hydropower.
2. Versatile: Green hydrogen is a flexible energy source that can be utilized for industrial operations, heating, and transportation.
3. Energy Storage: When it comes to controlling the erratic nature of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, hydrogen can be employed as an energy storage solution.
4. High Energy Density: Due to its high energy density, green hydrogen has a lot of energy in relation to its weight or volume.
5. Clean: Hydrogen is a clean and environmentally friendly energy source since its only byproduct is water.
Limitations of Green Hydrogen:
1. Cost: Green hydrogen production is currently more expensive than conventional fossil fuel-based energy options, which makes it less economically feasible.
2. Infrastructure: The infrastructure for hydrogen generation, distribution, and storage is currently lacking, which makes it difficult to increase the usage of green hydrogen.
3. Efficiency: Relatively little hydrogen can be produced with a lot of energy due to the low efficiency of the green hydrogen production process.
4. Safety: Because of its extreme flammability and the need for specific safety precautions during production, shipping, and storage, using hydrogen as an energy source can be more expensive and complicated.
5. Carbon Intensity of Grey Hydrogen: Grey hydrogen, or hydrogen produced from fossil fuels, emits a large amount of greenhouse gases and is very carbon-intensive, despite the fact that green hydrogen is a clean energy source.
Green Hydrogen Technologies
In contrast to conventional fossil fuel-based approaches, green hydrogen technologies refer to the several techniques and procedures used to manufacture hydrogen using renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydro power. Since there are no carbon emissions throughout the production process, green hydrogen is a clean, sustainable energy source that may be applied to a variety of industries.
Some of the key green hydrogen technologies include:
1. Electrolysis: Using an electric current, water molecules are split into hydrogen and oxygen during the process of electrolysis. This procedure is referred to as a “green hydrogen production method” when it is fuelled by renewable energy sources like solar or wind.
2. Biomass gasification: This process involves the conversion of organic matter, such as agricultural waste or wood chips, into a gas that is then used to produce hydrogen. When the organic matter is sustainably sourced and the gasification process is powered by renewable energy sources, this method can also be considered a green hydrogen production method.
3. Solar thermochemical: Through the use of concentrated solar energy, high temperatures necessary to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen are produced. Although this process is currently in the experimental stage, it has the potential to be a very effective and long-lasting way to produce green hydrogen.
4. Algae production: With the help of carbon dioxide emissions and sunshine, algae can grow and be collected to make hydrogen. Although this process is still in its infancy, it has the potential to be a scalable and sustainable green hydrogen generation technique.
5. Waste-to-hydrogen: Hydrogen can be created by the processing of certain waste products, such as sewage and landfill gas. Although this process is still in its infancy, it has the potential to be a green method of producing hydrogen that contributes to waste reduction and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
Green hydrogen technologies in the green hydrogen economy are anticipated to play an increasingly significant role in the global energy mix as the demand for clean energy sources increases. With the use of these technologies, hydrogen can be produced in a scalable and sustainable manner that can be applied to a variety of industries to aid in the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and the advancement of the low-carbon economy.
Uses of Green Hydrogen
Use of Green Hydrogen in Transportation Industry:
Green hydrogen has a wide range of potential applications across multiple sectors and is created utilizing renewable energy sources and techniques that limit carbon emissions. The following are some important uses for green hydrogen:
Clean and Energy Transportation:
1. Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs): Fuel cell vehicles can be powered by green hydrogen, providing a clean substitute for gasoline and diesel. FCVs are becoming more and more popular as a way to lower carbon emissions in the automobile industry.
2. Gas Pipelines: Renewable energy may be stored and transported over great distances by injecting green hydrogen into the natural gas pipes that are already in place.
Industrial Processes:
1. Automotive Industry: Green hydrogen is used to power hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs), which are produced and sold by companies including Toyota, Hyundai, and BMW. With their lengthy driving ranges and short refilling periods, these FCVs provide emission-free mobility.
2. Steel Production: The steel sector is investigating the possibility of using green hydrogen as a reducing agent in place of coking coal to lower carbon emissions throughout the steelmaking process.
Heating and Cooling:
1. Residential and Commercial Heating: Fuel cells can use hydrogen as a clean substitute for natural gas in heating and cooling applications.
Aircraft and Maritime Transport:
1. Aircraft: Research is being done on hydrogen as a possible aircraft fuel to lower emissions from the airline sector.
2. Maritime: The marine industry is currently investigating the use of green hydrogen in fuel cells for auxiliary power systems and propulsion as a clean fuel for ships. The ferry that runs on hydrogen is undergoing testing at the European Marine Energy Centre (EMEC).
3. Aviation: Green hydrogen is being investigated by the aviation industry as a sustainable aircraft fuel. For instance, the startup ZeroAvia is creating commercial aircraft powertrains that run on hydrogen.
Green Hydrogen usage in Industry and Manufacturing:
1. Chemical Industry: By using green hydrogen as a feedstock or energy source in a variety of chemical processes, the chemical industry can become less dependent on fossil fuels and move toward decarbonization.
2. Refining: Green hydrogen has the potential to mitigate the carbon intensity of petroleum refining by taking the place of fossil fuels in the process.
Green Hydrogen Opportunities in Energy and Power Generation Industry:
Energy Storage:
1. Grid Balancing: Through electrolysis, excess renewable energy can be converted into green hydrogen. When renewable energy sources aren’t generating any electricity, this hydrogen can be stored and used to create electricity, which will help to stabilize the system.
Power Generation:
1. Electricity Generation: Hydrogen is a dependable source of energy that can be utilized in fuel cells or used in gas turbines to produce electricity, particularly in areas with sporadic renewable energy sources.
2. Power-to-Gas: Green hydrogen can be produced using electrolysis in the power-to-gas process, which uses excess renewable energy. Hydrogen has multiple applications, such as electricity generation, and can be stored or injected into the natural gas grid.
Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Plants: Green hydrogen is a fuel that may be used in CHP facilities to produce heat and power efficiently. These facilities have the potential to aid in the decarbonization of the electricity and heat industries.
The potential of green hydrogen to decarbonize hard-to-electrify industries including heavy industrial, transportation, and heating is one of its main benefits. Green hydrogen can be used as a feedstock for chemical reactions, as fuel for fuel cell vehicles, or in substitution of fossil fuels in industrial processes like cement and steel manufacturing.
Other advantages of green hydrogen energy solutions include enhanced energy security, better air quality, and the creation of jobs in the clean energy industry. By offering a way to store extra renewable electricity for use during periods of high demand, they can also aid in the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid.
Green hydrogen energy solutions are anticipated to become more significant as the world moves toward a more sustainable energy future. The development of green hydrogen technologies and the green hydrogen economy is being funded by numerous nations and businesses worldwide, with the aim of mitigating the effects of climate change and reaching net-zero emissions.
Fundamentally, clean and renewable energy alternatives to fossil fuels are what green hydrogen energy solutions offer, paving the way for a more sustainable and just energy future for all.
Green Hydrogen Economy
A future economic system known as the “Green Hydrogen Economy” is one in which hydrogen, especially green hydrogen made from renewable energy sources, is essential to many different sectors and industries. It predicts a move away from fossil fuels and toward a growing reliance on hydrogen as a sustainable and green energy source.
1. Energy Export: Exporting green hydrogen from nations with an abundance of renewable energy resources to those with less promise for renewable energy can open up economic opportunities and promote international hydrogen trade.
2. Hydrogen Infrastructure: A thorough infrastructure for hydrogen, comprising production plants, distribution systems, and refueling or charging stations, must be developed in order to support the green hydrogen economy.
3. Research and Innovation: To increase the effectiveness and affordability of green hydrogen generation systems and broaden their range of applications, ongoing research and innovation are crucial.
One important aspect of international attempts to shift to a low-carbon and sustainable energy system is thought to be the green hydrogen economy. It addresses the need for energy storage technologies, greener energy sources, and a decrease in carbon emissions in line with environmental goals. However, in order to fully realize the promise of the green hydrogen economy, factors like production costs, infrastructure development, and guaranteeing a steady supply of renewable energy must be taken into account.
Leading players in Green Hydrogen Economy
Some of the leading players in the green hydrogen industry are:
1. Air Liquide: A French business that offers services and industrial gases to a range of sectors. It is a major player in the green hydrogen market, offering solutions for the production and delivery of hydrogen.
2. Linde: Offering solutions for hydrogen production and delivery, it has a major position in the green hydrogen industry.
3. Siemens Energy: A German business that offers different sectors energy solutions. It works on developing hydrogen-related technologies, such as green hydrogen storage and generation.
4. ITM Power: A UK-based business that develops and produces green hydrogen generation equipment as well as comprehensive hydrogen energy solutions.
5. Nel Hydrogen: A Norwegian business that offers hydrogen production, delivery, and storage options. With its electrolysis method for hydrogen production, it has a major position in the green hydrogen business.
6. Plug Power: A US-based business that offers stationary power and transportation applications among its many hydrogens fuel cell uses. It works on creating green hydrogen solutions for several sectors of the economy.
7. Ballard Power Systems: A Canadian business that offers fuel cell systems for stationary power and mobility, among other uses. It works to lower the cost of hydrogen fuel cells and is engaged in the development of green hydrogen technology.
8. McPhy Energy: A French enterprise offering production, distribution, and storage of hydrogen.
9. Green Hydrogen Systems: A Danish business that offers methods for producing hydrogen using electrolysis. It is aiming to lower the cost of producing hydrogen and is engaged in the development of green hydrogen technologies.
One of the most important factors in attaining a more sustainable and carbon-neutral future is the green hydrogen revolution. It supports international initiatives to cut greenhouse gas emissions and make the switch to a low-carbon economy. For widespread acceptance, it is crucial to address issues including production costs, infrastructure expansion, and providing a reliable and inexpensive supply of renewable energy.
Read More – https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/industry-practice/hydrogen/green-hydrogen