Normal
0
false
false
false
EN-US
X-NONE
X-NONE
/* Style Definitions */
table.MsoNormalTable
{mso-style-name:”Table Normal”;
mso-tstyle-rowband-size:0;
mso-tstyle-colband-size:0;
mso-style-noshow:yes;
mso-style-priority:99;
mso-style-qformat:yes;
mso-style-parent:””;
mso-padding-alt:0in 5.4pt 0in 5.4pt;
mso-para-margin-top:0in;
mso-para-margin-right:0in;
mso-para-margin-bottom:10.0pt;
mso-para-margin-left:0in;
line-height:115%;
mso-pagination:widow-orphan;
font-size:11.0pt;
font-family:”Calibri”,”sans-serif”;
mso-ascii-font-family:Calibri;
mso-ascii-theme-font:minor-latin;
mso-hansi-font-family:Calibri;
mso-hansi-theme-font:minor-latin;
mso-bidi-font-family:”Times New Roman”;
mso-bidi-theme-font:minor-bidi;}
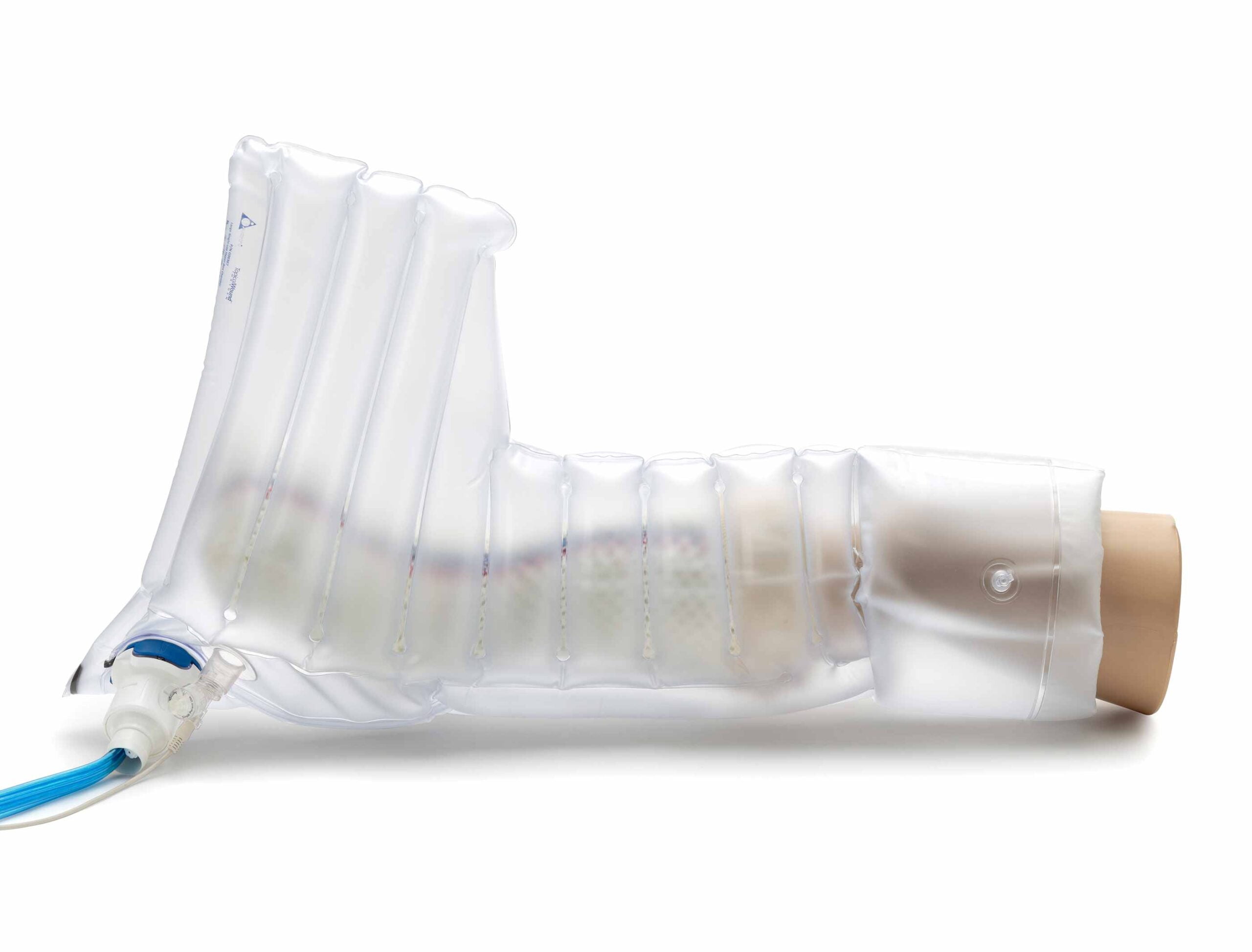
Venous leg ulcers, a prevalent chronic condition, result from impaired venous circulation, often due to venous insufficiency. These ulcers, typically located around the lower leg or ankle, demand specialized care and a comprehensive approach to facilitate healing and prevent recurrence.
Understanding Venous Leg Ulcers: Venous leg ulcers stem from venous insufficiency, where damaged valves impair blood flow, leading to pooling and increased pressure in the lower limbs. This chronic venous hypertension causes tissue damage and ulcer formation.
Identification and Diagnosis: Accurate diagnosis involves assessing the ulcer’s characteristics, location, size, and surrounding tissue. Determining the underlying venous insufficiency guides treatment strategies.
Treatment Approaches:
- Compression Therapy: Graduated compression bandages or stockings aid in reducing edema, improving venous return, and promoting ulcer healing.
- Wound Bed Preparation: Proper wound care involves cleansing the ulcer, applying specialized dressings to foster healing, and managing infection risks. Debridement may be necessary to promote granulation tissue formation.
- Vascular Interventions: Some cases may require vascular procedures to address underlying venous insufficiency.
Multidisciplinary Collaboration: Collaboration among healthcare professionals, including vascular specialists, wound care experts, nurses, and physical therapists, ensures a comprehensive approach tailored to individual needs.
Preventive Measures and Long-Term Care: Preventing recurrence involves ongoing management of venous insufficiency through compression therapy, lifestyle modifications, and patient education on proper wound care techniques. Regular monitoring helps in preventing complications.
Patient Education and Empowerment: Educating individuals on preventive measures, warning signs of worsening ulcers, and the importance of adherence to treatment plans empowers them to actively participate in their care and promotes better outcomes.
Impact on Quality of Life: Venous leg ulcers can significantly affect an individual’s mobility, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life. Addressing both the physical and psychological aspects is crucial for holistic care.
Research and Advancements: Continued research and technological advancements aim to improve treatment modalities, reduce healing times, and enhance outcomes for individuals affected by venous leg ulcers.
Managing venous leg ulcers demands a comprehensive, proactive, and patient-centered approach.